tests for intestinal permeability|does leaky gut cause diarrhea : member club The Array 2 Intestinal Antigenic Permeability Screen™ is an important initial screening test for patients with multiple chronic GI and neurologic symptoms, suspected food sensitivities, chemical intolerances, or a history of . 提示:版微信需要使用浏览器Cookie来帮助你登录,以便运行版应用程序。 详细信息 版微信需要配合手机使用
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB192.168.1.7 您设备的路由器登录名和密码 192.168.1.7 我们将帮助您进入路由器或网络上的其他设备 192.168.1.7 是用于本地网络的私有 IP 地址。 您可以通过在浏览器的地址栏中输入 192.168.1.7 来登录管理页面。
Leaky gut syndrome is a hypothetical condition. It’s based on the concept of relative intestinal permeability. See more
There are diseases that are known to be associated with intestinal permeability, and there is a lot of speculation about other possible diseases that might be . See moreThe known causes of intestinal permeability involve systematic erosion of the intestinal lining. This is not a simple feat. Your intestinal lining has many layers of . See more
Erosion of your intestinal lining is one thing, and intestinal permeability is another. Most people who think they may have a leaky gut have certain common . See more The Array 2 Intestinal Antigenic Permeability Screen™ is an important initial screening test for patients with multiple chronic GI and neurologic symptoms, suspected food sensitivities, chemical intolerances, or a history of .There are two primary methods used clinically to assess leaky gut: the lactulose/mannitol permeability assay (through Genova, covered here), and the antigenic permeability screen .Standard light microscopy of Hematoxylin & Eosin (H&E) stained intestinal sections is able to detect intestinal pathology including ulcerations of the mucosa and severe intestinal .
When it comes to assessing if a patient has Intestinal Hyper-Permeability, or Intestinal Barrier Penetration, a.k.a. “Leaky Gut”, there are currently only a handful of reliable lab tests that are used. Definition of intestinal permeability and intestinal barrier. The term "mucosal barrier" was adopted by Cummings in 2004 to describe the complex structure that separates the internal milieu from the luminal environment [].The physical barrier includes a cellular component consisting of the vascular endothelium, the epithelial cell lining, and the mucus layer.We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
aggregate impact value test as per is code
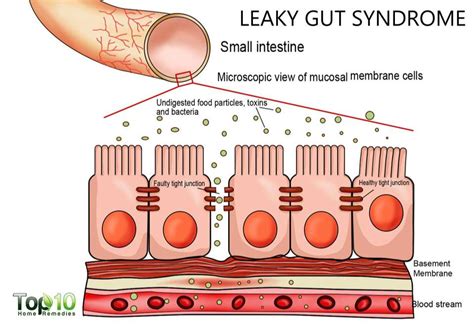
Increased intestinal permeability owing to tight junction barrier loss could be targeted in gastrointestinal diseases associated with increased permeability. . In vitro testing identified one .A stool analysis assesses digestive function, intestinal inflammation, and the intestinal microbiome, which may contribute to symptoms. In addition to common gastrointestinal complaints, clinicians often assess gut health for numerous other conditions including autoimmune diseases, mood disorders, skin and others.
Using a collection of innovative biomarkers, this test helps clinicians determine if their patients have intestinal permeability, or “leaky gut.” Intestinal permeability has been suggested as a root cause of autoimmune diseases, systemic inflammation, and food sensitivities. Healing the gut barrier is so pivotal for resolving chronic .
in the intestinal permeability test [4–6, 8, 9]. E.g., in a study by Ahmed and colleagues, the DIO mice gained 130% of their initial weight while the lean mice gained 30%, and the DIO mice We already know that increased intestinal permeability plays a role in certain gastrointestinal conditions such as celiac disease, Crohn's disease, and irritable bowel syndrome. The biggest question is whether or not a leaky gut may cause problems elsewhere in the body. Some studies show that leaky gut may be associated with other autoimmune .The objectives of this review on 'leaky gut' for clinicians are to discuss the components of the intestinal barrier, the diverse measurements of intestinal permeability, their perturbation in non-inflammatory 'stressed states' and the impact of treatment with dietary factors. Information on .Using a collection of innovative biomarkers, this test helps clinicians determine if their patients have intestinal permeability, or “leaky gut.” Intestinal permeability has been suggested as a root cause of autoimmune diseases, systemic inflammation, and food sensitivities.
what causes increased intestinal permeability
The role of intestinal permeability in the pathogenesis of immune-mediated diseases is a relatively new field of translational science that only recently has received proper attention. While the zonulin pathway is the only physiologic mechanism described so far, it is likely that other pathways are involved in physiologic TJ modulation. . A possible cause of leaky gut is increased intestinal permeability or intestinal hyperpermeability. . too. And tests often fail to uncover a definite cause of the problem. That can leave people . In future, LM test to assess intestinal permeability in children can be simplified by shortening the urine collection time from 5 hours to 2 hours. Introduction. The lactulose: mannitol (LM) test is a quantitative assay for directly measuring the ability of two non-metabolized sugar molecules—lactulose and mannitol—to permeate the .
The Leaky Gut Test (or Intestinal Permeability Test) is a noninvasive gastrointestinal test that measures small intestinal absorption and barrier function in the bowel. Malabsorption and increased intestinal permeability (leaky gut) can be .Intestinal permeability, together with luminal antigen (Ag) sampling by enterocytes via the transcellular pathway and dendritic cells, regulates molecular trafficking between the intestinal lumen and the submucosa, leading to either tolerance or immune response to non-self Ag 3– 5 ( Figure 1). Intercellular tight junctions (TJs) tightly . How This Leaky Gut Test is Done: . An intestinal permeability assessment can also measure the ability of two sugar molecules to permeate the gut lining — lactulose and mannitol. This leaky gut test checks for levels of .
Intestinal barrier permeability may therefore be a prognostic marker for disease pathophysiology; similarly, targeting the intestinal barrier permeability holds promise for therapy and for the . Testing of intestinal permeability is not required for routine patient care, however it is an important tool to understand the function of the paracellular transport in the research setting. Increase in intestinal permeability has been implicated in the pathogenesis of many autoimmune diseases including celiac disease, Crohn's disease, type I .
Leaky gut is also something that is not diagnosable with stool tests or blood tests. No test is universally recognized as reliable in diagnosing intestinal permeability. Some specialized testing is being studied, but there isn't enough information yet to use these tests in patients with any certainty.
Leaky gut syndrome is a collection of symptoms attributed to the idea that the intestinal barrier is impaired, allowing toxins from the intestines (the "gut") to enter the bloodstream. Background A widely used method in assessing small bowel permeability is the lactulose:mannitol test, where the lactulose:mannitol ratio (LMR) is measured. However, there is discrepancy in how the test is conducted and in the values of LMR obtained across studies. This meta-analysis aims to determine LMR in healthy subjects, coeliac and Crohn’s disease. . Intestinal permeability is an important diagnostic marker, yet its determination by established tests, which measure the urinary excretion of orally administered tracer molecules, is time consuming and can only be performed prospectively. Here, we aim to validate proposed surrogate biomarkers, which allow measuring intestinal permeability more easily. In this .
aggregate impact value test astm

The objectives of this review on ‘leaky gut’ for clinicians are to discuss the components of the intestinal barrier, the diverse measurements of intestinal permeability, their perturbation in non-inflammatory ‘stressed states’ and the impact of treatment with dietary factors. Information on ‘healthy’ or ‘leaky’ gut in the public domain requires confirmation before endorsing .Intestinal permeability tests have been used to screen for a wide range of small intestinal diseases, including coeliac disease and enteric infections. Several probe molecules have been used to investigate intestinal permeability including monosaccharides, disaccharides, 51Cr-EDTA and polyethylenegl . The innocuousness and easiness of intestinal permeability tests can be explored to expand the knowledge about the clinical situations in which intestinal barrier dysfunction can be an important feature. Many factors may influence the results of the test. Researchers and healthcare professionals should try to circumvent the possible pitfalls of .indicative of intestinal permeability. The changed ratio can have several causes: Increased lactulose absorption via the paracellular route. This may be due to decreased villous height or impaired function of tight junctions. Decreased mannitol absorption due to decreased surface areas of gut villi. Causes of Intestinal Permeability
About the Test. The Intestinal Permeability Assessment directly measures the ability of two non-metabolized sugar molecules to permeate the intestinal mucosa. It assesses small intestinal absorption and barrier function in the bowel to help diagnose malabsorption and intestinal permeability/leaky gut. Here, we describe an ex vivo intestinal permeability assay, X-IPA, for quantitative analysis of gut permeability dynamics at the whole-tissue level. . Statistical significance between two groups .
urine test for leaky gut
intestinal permeability test at home
intestinal antigenic permeability screen
Resultado da 1,694 Followers, 4,613 Following, 40 Posts - See Instagram photos and videos from Vassoler Sport Lazer (@vassoler.sportlazer)
tests for intestinal permeability|does leaky gut cause diarrhea